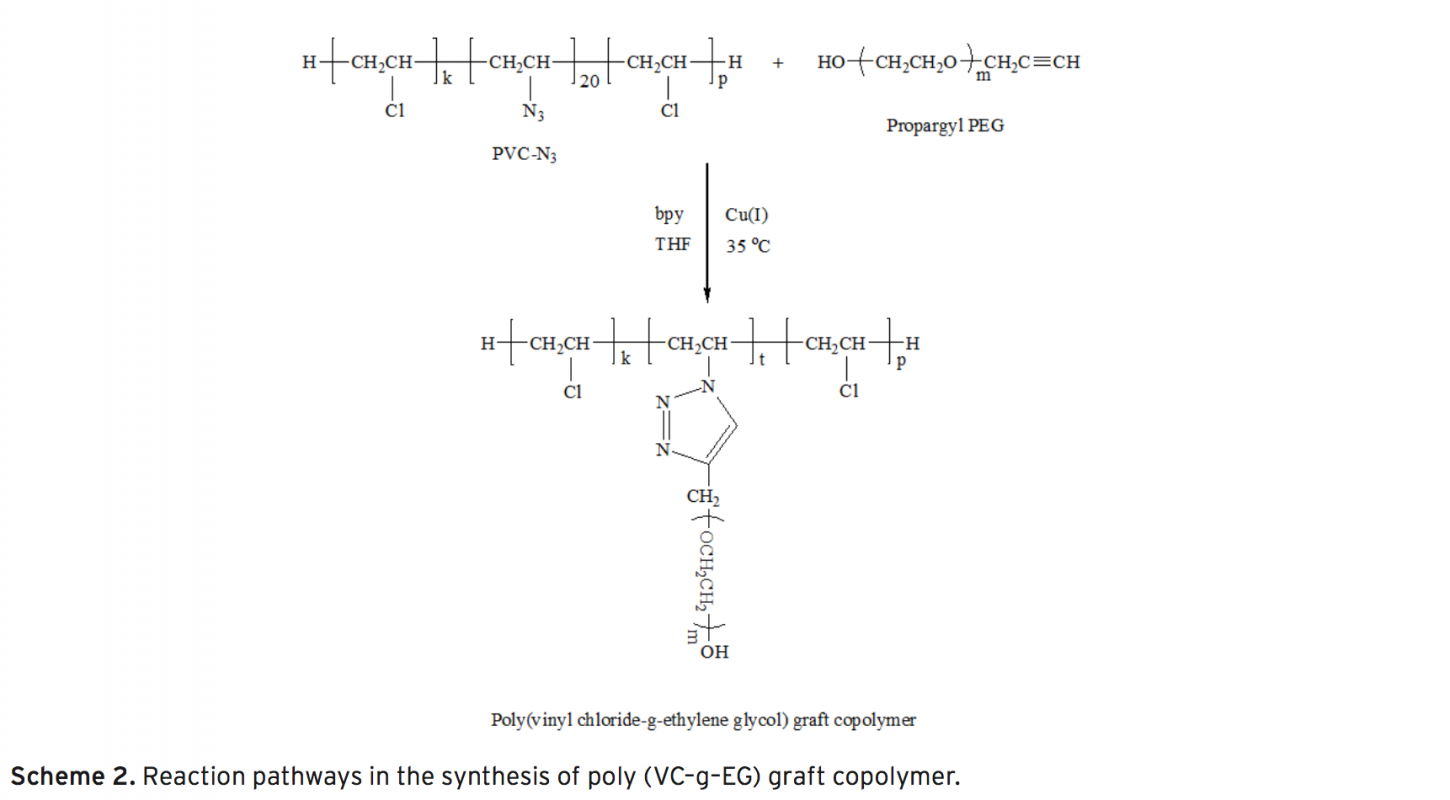
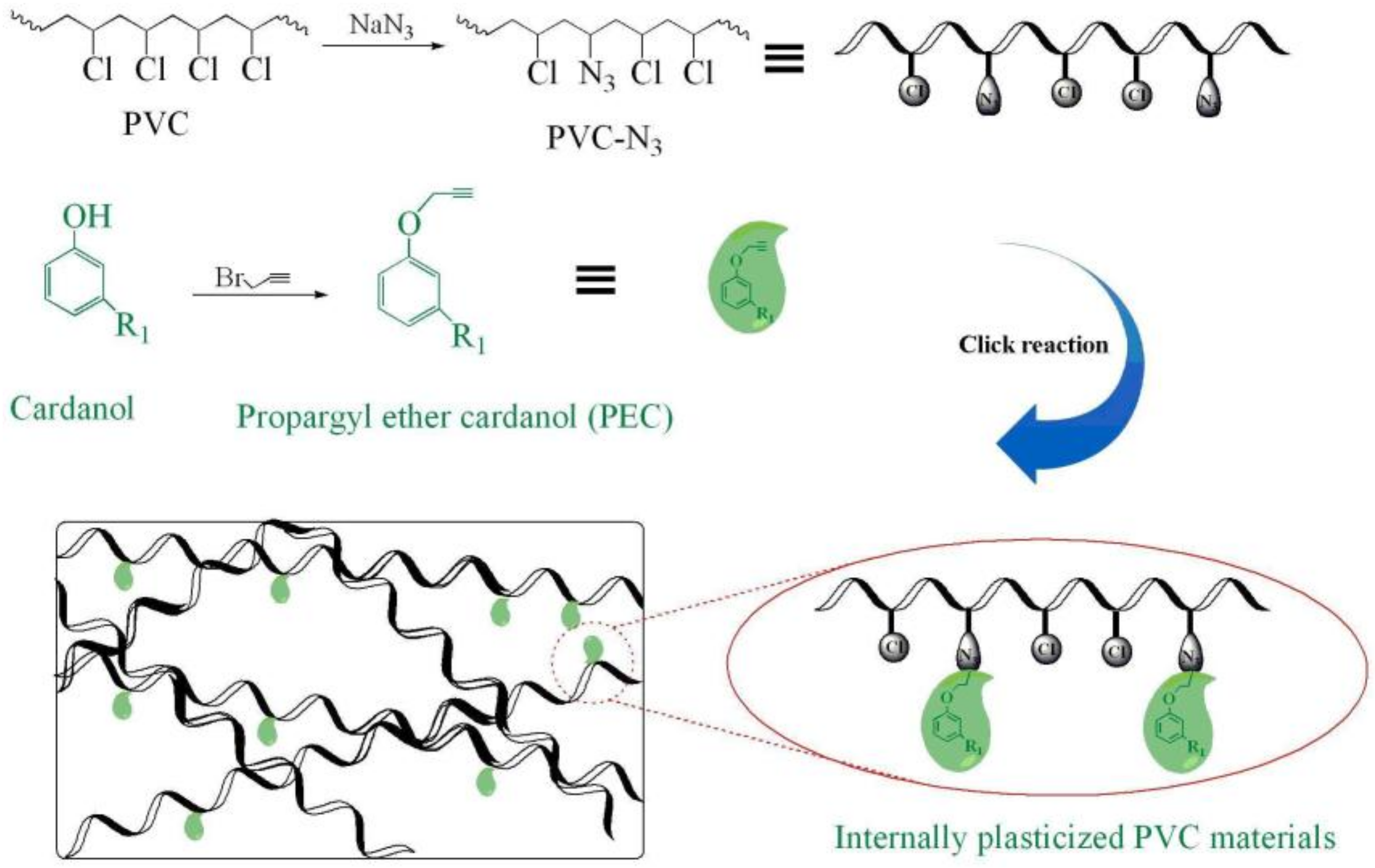
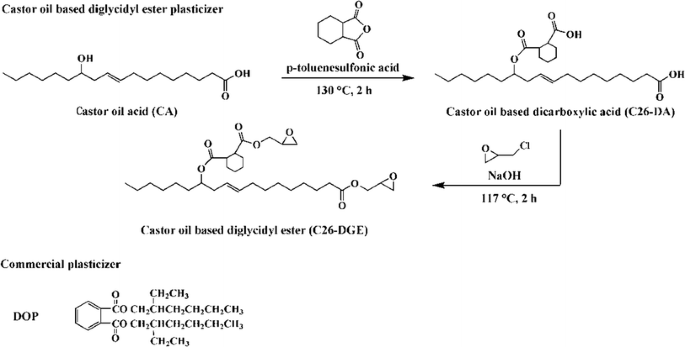
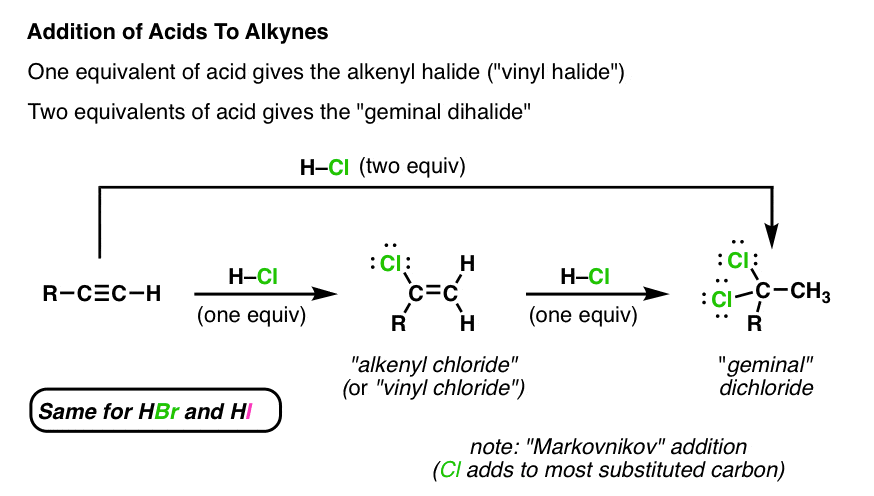Synthesis Of Vinyl Chloride
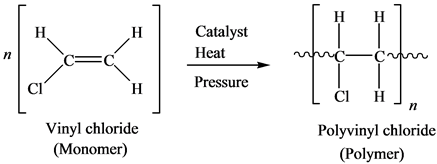
In the vinyl chloride example emphasis was placed on the synthesis steps and not on the use of heuristics by the design team.
Synthesis of vinyl chloride. Amounts of copper iodide and trans n n dimethylcyclohexane 1 2 diamine in the presence of tetramethylammonium chloride or bromide enables the transformation of easily accessible alkenyl iodides into their far less available chlorinated and brominated derivatives in excellent yields and with full. Vinyl chloride was first produced using the process of dehydrating ethylene dichloride edc with alcoholic caustic potash. Huang synthesis 2004 1557 1558. Thermal decomposition of dichloroethane.
In one ethylene is converted to 1 2 dichloroethane ethylene chloride by reaction with chlorine. However the first effective industrial process was based on the hydrochlorination of acetylene. Second only to polyethylene among the plastics in production and consumption pvc is used in an enormous range of domestic and industrial products from raincoats and shower curtains to window frames and indoor plumbing. Synthesis of vinyl bromides.
Ethane sulfochlorination has been proposed as a route to produce vinyl chloride using sulfur instead of oxygen. Vinyl chloride can also be obtained as a byproduct in the synthesis of chlorofluorocarbons when saturated chlorofluorocarbons are catalytically dechlorinated by ethylene. Under pressure the gaseous chloroethene molecules are forced closer together to form a liquid. The monomer chloroethene or vinyl chloride has a boiling point of 14 o c 259k so it is a gas at room temperature and pressure.
A metal free regio and stereoselective method provides e configured α halo enamides vinyl thioethers and vinyl ethers using aqueous hx x f cl br i. This example shows the steps in syn task integration fig figure 4 9 inverted synthesis tree for the production of viny. Polyvinyl chloride is produced in an addition polymerisation reaction from chloroethene vinyl chloride monomers. Heating 1 2 dichloroethane in the presence of a charcoal catalyst gives vinyl chloride.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced by polymerizationof the vinyl chloridemonomer vcm as shown. About 80 of production involves suspension polymerization. The major industrial preparation of vinyl chloride begins with ethylene and has two variants. Prospects for using the known methods for controlled synthesis of macromolecules to obtain vinyl chloride homo and copolymers under the conditions close to those of industrial processes are.
The method offers high functional group compatibility and regio and stereoselectivity mild conditions high efficiency and rapid. Chloride tree is closely related to any heuristics or rules of thumb used by the design team. Published data on controlled synthesis of polyvinyl chloride and of copolymers of vinyl chloride with other monomers under the conditions of radical initiation and coordination catalysis are analyzed.